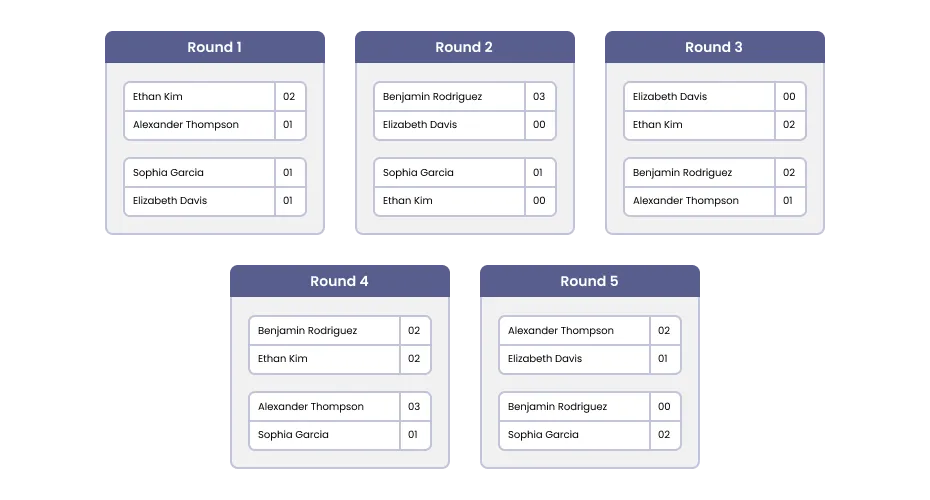
In round-robin tournaments, participants play one another in a round-robin format. A bracket like this is commonly used when there are many participants and a limited time.
It is possible to determine the top competitors in a tournament thoroughly and fairly using a round-robin bracket. A bracket reduces the chances of upsets or competitors advancing without being tested. When a competitor loses in a single elimination bracket, he or she is eliminated.
As more matches are played and spectators have more chances to see each competitor in action, round-robin brackets can also be more spectator-friendly. As a result of this format, assignments can be more flexible since consecutive matches are not required.
Round-robin brackets are played twice; double round-robin brackets are played three times; and triple round-robin brackets are played four times per participant. How many rounds will be played in the bracket depends on the number of participants and the amount of time available for the tournament.
Sporting and other competitive events commonly use round-robin brackets as a method of determining who the best competitors are.
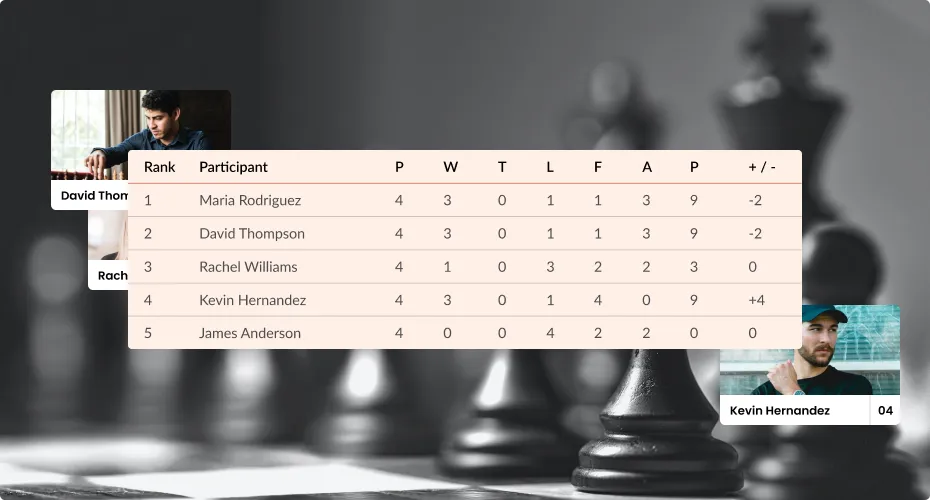
Winners are determined by their records. If a tie occurs, there are a few different ways to determine the winner, depending on the tournament rules:
- In a knockout bracket, the top players or teams are seeded.
- A point differential determines the winner. Single round-robin ties are broken based on head-to-head records. Chess, for example, is an exception.
- It may be necessary to play a final head-to-head game if both teams have an equal record against each other.
Typically, three teams can participate in a round-robin tournament. Because each team must play every other team, the longer (and more time-consuming), the tournament will be.